Current location: Home > NEWS > Industry news
NEWS
PRODUCTS
Exploring the Role of HRD in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Endometrial Cancer
News source: Release time:[2025-11-12]
?
Uterine cancer ranks as the sixth most prevalent cancer globally in terms of new female cases. In 2022, there were 420,000 reported instances, constituting 4.3% of all female malignant tumors, with endometrial cancer being the primary type. For individuals with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer, conventional treatments offer limited efficacy, and the prognosis is typically grim. The use of homologous recombination repair defects (HRD) in treating ovarian cancer is widely recognized. However, recent research data have shed light on the potential for exploring and applying HRD in the context of endometrial cancer.
01. First understand: What is HRD? What does it have to do with cancer?
Before we delve into Human Resource Development (HRD), let's begin by examining the "DNA repair system" of cells. The cells in our bodies are perpetually dividing and renewing each day. During this process, DNA inevitably sustains damages, such as "double-stranded breaks." This constitutes a severe form of DNA damage. If the repair process is not prompt or accurate, it may result in gene mutations and potentially even cell carcinogenesis.
Homologous recombination (HR) serves as a "precise tool" for cells to mend DNA double-strand breaks. Much like a skilled craftsman, it utilizes homologous chromosomes as a template to accurately repair the broken DNA, thereby preventing the accumulation of errors. However, should the HR repair function "fail," this condition is referred to as "homologous recombination defect (HRD)."
When HRD occurs, cells must depend on alternative, less precise repair methods, such as non-homologous end-to-end ligation, to repair DNA. This reliance can lead to a multitude of genetic mutations and chromosomal abnormalities, ultimately resulting in cancer.
02. Which subtypes of HRD are preferred in endometrial cancer? How high is the incidence?
1.HRD prefers non-endometrial-like cancer (NEEC).
In a study published in the 2019 Journal of Clinical Cancer Research [2], Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) was measured in 25 patients with endometrial cancer. It was found that HRD was mainly concentrated in non-endometrioid-like cancers (NEECs), with an incidence rate of 46%, while none of the endometrioid-like cancers (EECs, the most common subtype) exhibited HRD (P=0.014).
NEEC is a highly malignant subtype of endometrial cancer, encompassing serous cancer, carcinosarcoma, and clear cell cancer. The prognosis for these patients is often poor. The study also found that nearly all NEECs with HRD carry TP53 gene mutations (100%), suggesting that the TP53 mutation combined with the NEEC pathological type may be an important indicator of HRD.
To verify this conclusion, the researchers also analyzed endometrial cancer data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The results were highly consistent with their own research: the incidence of BRCA-related genomic scars (the "molecular imprint" of HRD) in NEECs from TCGA was as high as 48%, whereas that of EEC was only 12% (P<0.001). This further confirms that HRD is more common in highly malignant endometrial cancer subtypes.
2. HRD distribution of different molecular subtypes: CN-H and CN-L subtypes are the "main force"
In the summary of this year's ASCO meeting [3], domestic scholars also elaborated on this type of data. In this study, 372 patients with endometrial cancer were tested for HRD (the HRD score is calculated based on LOH, TAI, and LST). The results revealed in more detail the distribution of HRD in different molecular subtypes:
· Overall incidence: 10.75% of patients with endometrial cancer have a positive HRD score, and 5.38% of patients carry a BRCA1/2 gene mutation (core genes of the HR repair pathway);
· Subtype preference: HRD positivity was mainly concentrated in the "high-copy (CN-H)" and "low-copy (CN-L)" subtypes, accounting for 4.57% and 2.96%, respectively; in the "POLE mutation" subtype, the positive rate of HRD is extremely low, almost zero.
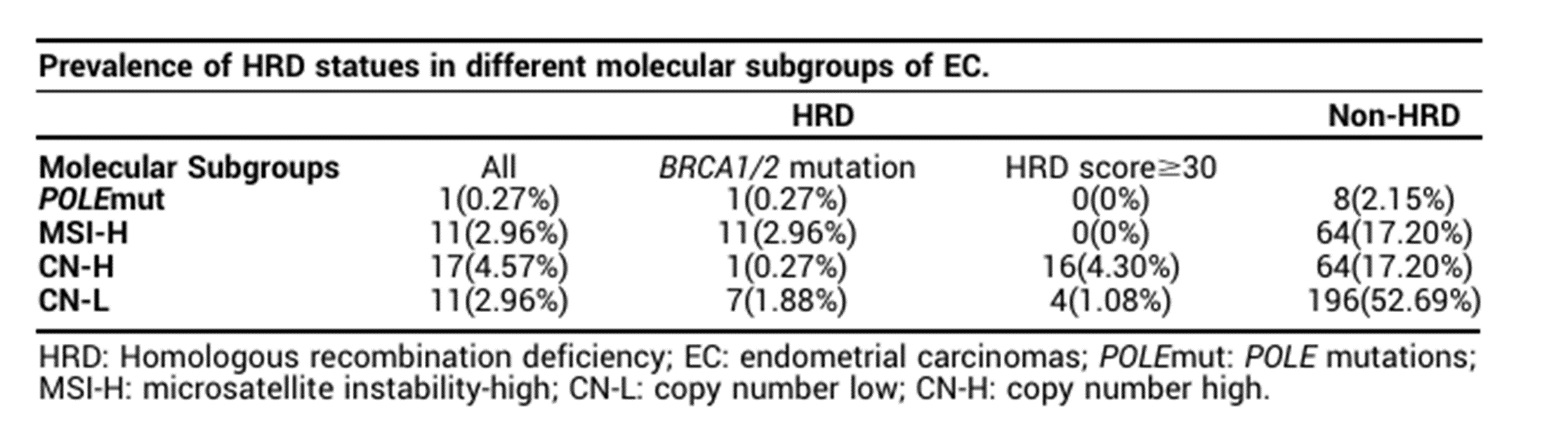
Table 1. Distribution of HRD status among different molecular subtypes in patients with endometrial cancer
In summary, HRD is not a "common feature" of endometrial cancer but is more prevalent in subtypes with high malignancy and poor prognosis. Consequently, HRD testing can assist doctors in rapidly identifying high-risk patients who "may benefit from PARPi treatment."
03.HRD detection: What practical assistance can it provide to patients with endometrial cancer?
For patients with endometrial cancer, detecting Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) is by no means a "redundant examination." It can provide practical benefits to patients in various aspects, including treatment selection and predicting treatment efficacy, particularly for those with advanced or recurrent disease.
1. Medication guidance: screening population benefiting from PARP inhibitors
Currently, there are two primary categories of "star drugs" for HRD tumors: platinum-based chemotherapy agents, such as cisplatin and carboplatin, and PARP inhibitors, including Olaparib and Niraparib. HRD testing assists physicians in determining a patient's eligibility for these drugs.
PARP inhibitors are particularly effective against HRD tumors. They work by inhibiting the PARP enzyme, thereby hindering tumor cells from repairing single-strand DNA breaks. However, HRD tumors lack the ability to repair double-strand breaks. Consequently, under this dual assault, tumor cells succumb to "DNA damage overload" and die.
The effectiveness of PARP inhibitors in HRD-positive patients has been substantiated by various clinical trials, including those involving endometrial cancer. For instance, results from the UTOLA trial, published in Nature Communications in 2025 [4], indicated that while maintenance therapy with Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor, did not significantly improve progression-free survival (PFS) across all patients, it notably extended PFS in the HRD-positive subgroup (5.4 months for the Olaparib group versus 3.6 months for the placebo group, HR=0.59, 95% CI 0.35-1.00). Even more strikingly, in patients with HRD who were "fully responsive to initial chemotherapy," Olaparib exhibited a more pronounced effect, with a median PFS of 8.8 months, nearly double that of the placebo group (3.8 months).
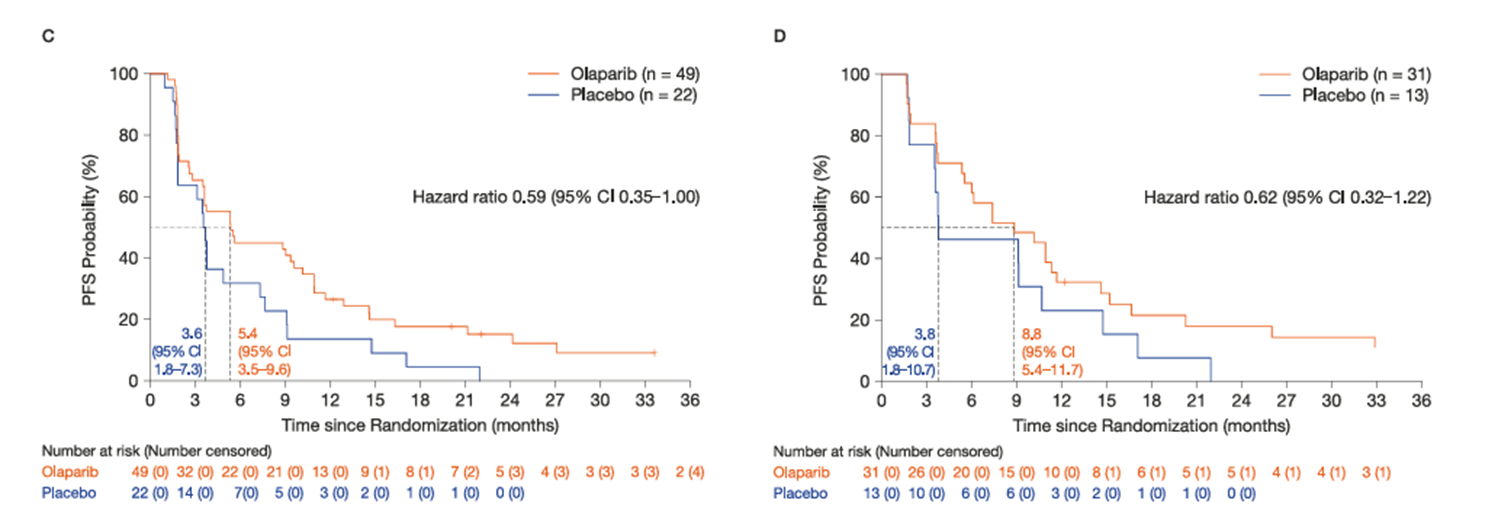
Figure 1. PFS data and survival profiles by subgroup A:
HRD positive subgroup; B: Complete response group to initial chemotherapy
2. Explore the combination of HRD type tumors and other treatments
In addition to PARP inhibitors and platinum-based chemotherapy, HRD may also exhibit "synergistic effects" with other treatments, such as immunotherapy. For instance, HRD-type tumors typically possess a higher number of gene mutations (a high tumor mutation burden), which enhances the tumor's "immunogenicity" and makes immunotherapy (such as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors) more effective. Currently, clinical trials (including the DUO-E study) have investigated the efficacy of "PARP inhibitor plus immunotherapy" in endometrial cancer. Preliminary results indicate that this combination is significantly effective in patients with positive HRD and pMMR [4]. Looking ahead, as more combined treatment strategies are explored, patients with HRD will have an expanded array of treatment options.
Summary
For patients with endometrial cancer, particularly those at high risk with advanced stages, recurrence, or pathological types such as NEEC and CN-H subtype, the HRD test can assist doctors in determining whether patients are candidates for PARP inhibitors or platinum-based chemotherapy, and also offers a reference for future combination treatments.
References
[1] J Natl Cancer Cent. 2024 Feb 2; 4(1):47-53.
[2] Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 1; 25(3):1087-1097.
[3] Meeting Abstract: 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting I
[4] Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 26; 16(1):7950.
Statement: This article is only for sharing, if it involves copyright issues, please contact us as soon as possible, we will correct the first time, thank you!